Controlling or control is an essential function in management. It is interrelated with other management functions as well. In simple words, the controlling function means a managerial function that compares actual performance in the organization with planned activities. This function helps managers identify any mistakes or errors and mitigate the risks of their plans. This chapter briefly describes some important areas about controlling. This chapter includes the meaning of controlling, the importance, levels of controlling, the process, and finally, types of controlling.
Meaning of controlling
The controlling function can be defined as a managerial process evaluating actual performance in the organization as per the planned performance. This function confirms that organizational activities are performed to achieve goals and objectives according to the plans. And if there any issues with the current progress, this will help to take corrective actions. Therefore the controlling can be identified as a primary goal-oriented function in the management process.
After the planning, this is the most crucial function in management. Every manager in an organization should be engaged with this control function; they perform the progress as planned. The controlling works as a backward-looking function to bring the management back to the planning. Therefore, controlling is an essential function for organized living as well as a living organization.
Importance of controlling
When considering the importance of controlling, it plays a significant role in achieving organizational goals. Without this function, any organization cannot be committed its goals and objectives according to the plans. A good control function helps an entity in many ways, such as,
- It helps to accomplish organizational goals and objectives by performing controlling.
- Help managers to identify irregularities such as cost overrun, employee turnover, and product defects.
- Easy to find better opportunities
- Manage complex situations in the organization as well as its environment.
- Organizational resources are utilized with effectiveness and efficiently
- Motivates employees and their productivity
- Lower-level managers can involve with decision-making.
Advantages of controlling
- The organization will able to reach its goals and objectives easily
- The quality of the products increases
- Employee motivation increases, and it will be led to an increase in productivity.
- Easy to find mistakes/errors in the planning function and manage risks
- Optimum utilization of organizational resources
- Every manager can make decisions at the right time in the right ways.
Process of controlling
The process of controlling consists of four main steps. They establish standards, measure actual performance, compare actual performance with standards, and take corrective actions to correct deviations.
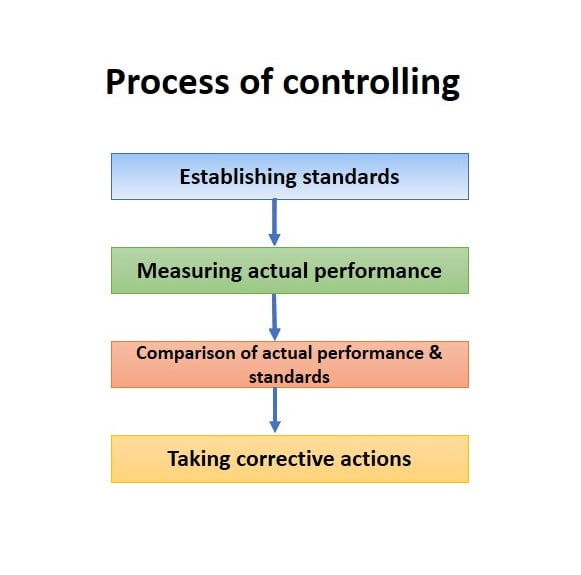
1.Establishing standards
As the first step in the control process, this involves setting up future targets which need to be accomplished to reach expected performance. Setting up standards is also a part of the planning process in management. There are different standards such as time standards, cost standards, income standards, market standards, and personal quantitative standards.
2.Measuring actual performance
This step can be referred to as a task of computing and evaluate the actual performance. This is a continuous task, and it involves collecting information that represents the actual performance. The evaluation of actual performance is compared with the expected performance/standards. And also, different methods can be used to measure the performance. The plans include ratio analysis, computerized devices, statistical analysis, personal observation, and strategic control points.
3.Comparing actual performance with standards
This is a task of comparing actual performance against standards. Because of this comparing, the management will understand the difference between actual performance and the expected performance. If there any wrong things/ deviations, the administration must be involved with corrective actions. When management makes this comparison, they use some methods to present comparison results. The methods are story method (assessments of variables, a form of written reports), layout method, graphical method, and mathematical method.
4.Taking corrective actions
After comparing the actual performance with established plans, the comparison results can be equal with the standards, higher or lower. If there are deviations, the management needs to take corrective actions. When considering corrective actions, they can be divided into three alternatives such as,
- Maintaining existing situation
If the actual performance is equal to standards, the management needs to continue the current situation.
- Correct the deviation
If the actual performance is lower than the standards, the management must be done to correct deviation/deviations.
- Change the standards
If the actual performance is higher than the standards, it is better to change standards.
NOTE: the deviations may be positive or negative
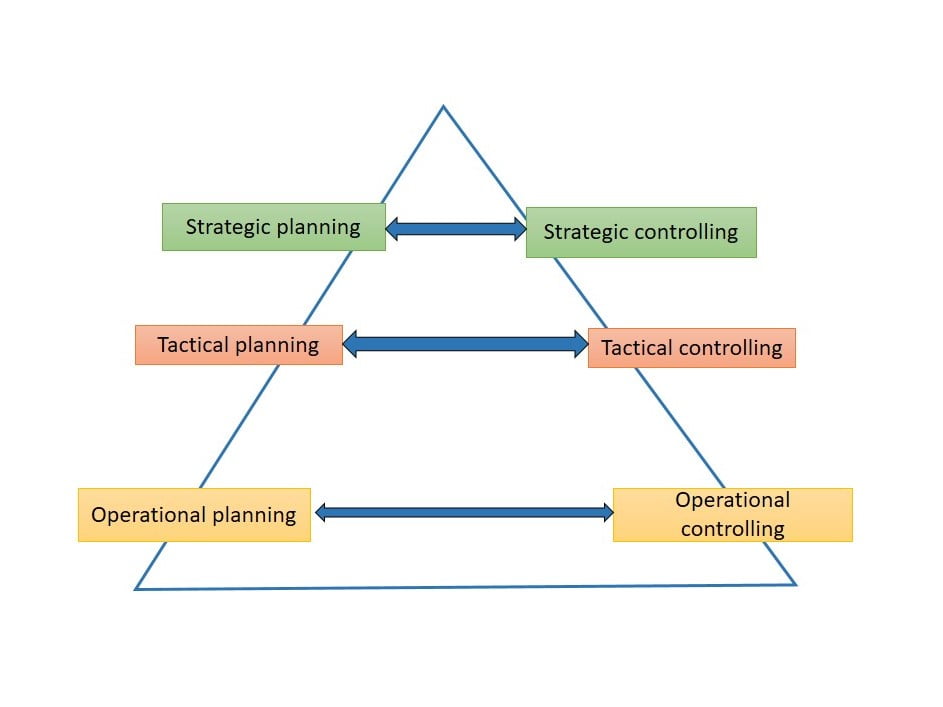
Levels of controlling
In management, there are mainly three different levels of control. It includes strategic control, tactical control, and operational control.
Strategic control
Strategic control is a process used by companies to control the implementation and development of strategic plans. Top-level management in an organization involves this strategic control process and is mainly focused on achieving long-term future goals.
When doing strategic controlling, the management needs to make sure that the tactical and operational plans are being executed as planned at both middle & lower management levels.
Mainly, there are four types of strategic controls: premise control, implementation control, strategic surveillance, and special alert control.
Tactical control
While strategic control focuses on achieving the long-term goal, tactical control involves tactical plans to reach that goal. Middle managers in the company mainly involve with tactical control and implement tactical plans at every departmental level.
They concentrate on middle-term time frames (weekly & monthly) and monitor periodical results to take corrective actions when there is a necessity.
Operational control
Operational control involves implementing operational plans. It regulates day-to-day results and is concerned with rules: budgets, schedules, and specific outputs. And also take corrective actions as necessary.
Operational control is a responsibility of lower-level management in the organization.
Interaction between the level of control and planning
Types of control
There are various types of controls in controlling function. They are feedforward control, concurrent control, and feedback control.
Feedforward control
Feedforward control, also known as preliminary control, is referred to controls, which are future-directed and designed to ensure the quality of the inputs (materials, human, information, financial resources).
These feedforward controls attempt to identify deviations and take corrective actions before they occur.
Concurrent control
The concurrent controls, alternatively known as screening control, can be referred to as a control applied into the operations while transformation is proceeding. Concurrent controls allow management to identify deviations during the transforming process and use corrective actions.
Feedback control
Feedback control, also called post-action control, concentrates on the organization’s outputs and examines the completed task and the feedback of the outcomes. But the problem of this feedback control is, the organization unable to take corrective actions when there is a defect in output. But this type of control is helpful to managers for planning future and performance evaluation.
Conclusion
- Controlling or control is the managerial function that compares actual performance in the organization with planned activities.
- This function confirms that organizational activities are performed to achieve goals and objectives according to the plans. And if there any issues with the current progress, this will help to take corrective actions.
- The controlling function plays a significant role in achieving organizational goals.
- Establishing standards, measuring actual performance, comparing actual performance with standards, and taking corrective actions to correct deviations are the five steps in the controlling process.
- There are mainly three levels of control: strategic control, tactical control, and operational control.
- Feedforward controls are future-directed and designed to make sure about the quality of the inputs.
- The concurrent controls are control that can be applied to the operations while transformation is proceeding.
- Feedback control concentrates on the organization’s outputs and examines the completed task as well as the feedback of the outcomes.





